Do I Actually Qualify for R&D Credits? A Manufacturer's Guide
"Do I actually qualify for R&D credits?" It's the question we hear constantly from manufacturers. Here's the key insight that might surprise you: If you're making or improving products, processes, or tooling—even to meet specific customer requirements—you probably do qualify!
Luzer Szimonowitz
Tax Preparer - Client Rep
Published: June 16, 2025
The Question Every Manufacturer Asks
There's a common misconception that R&D tax credits are reserved for high-tech pharmaceutical companies or software giants. The reality is that the R&D tax credit is designed to incentivize innovation and problem-solving in any business undertaking qualifying activities, and the manufacturing sector is absolutely brimming with this kind of ingenuity.
Key Insight
Most manufacturers are genuinely surprised by how broad the qualifications for R&D tax credits actually are. Every day, manufacturers are pushing boundaries, refining techniques, and developing solutions to complex challenges. This is the very essence of R&D.
- •That new jig you designed to speed up assembly? Potential R&D.
- •Modifications to enhance product performance? Likely qualifies.
- •Efforts to reduce waste on your production line? Could be R&D.

The Qualification Reality Check: Beyond the Lab Coat
One of the biggest hurdles in understanding manufacturing R&D credits eligibility is the pervasive "lab coat myth." When people hear "Research and Development," their minds often jump to images of scientists with bubbling beakers and complex chemical formulas. While that's certainly one face of R&D, it's far from the only one.
In Your Manufacturing Business, R&D Looks Like:
- • Designing new, more robust components for demanding applications
- • Experimenting with different materials to reduce costs
- • Developing more efficient production line layouts
- • Modifying machinery to perform new tasks
- • Creating custom solutions for specific customer requirements
- • Improving product quality and consistency
- • Reducing waste and energy consumption
- • Integrating new automation systems
Industry Reality Check
The good news is that the government recognizes this. Industry reports consistently show that a significant portion of all R&D tax credits are claimed by manufacturing companies. Some statistics suggest that manufacturers account for over 60% of successful R&D claims.
This isn't an accident; it reflects the inherently innovative nature of the manufacturing sector. You are constantly seeking ways to do things better, faster, and more cost-effectively.
Common Misconceptions Debunked
"We just do routine production."
While day-to-day, unchanged production doesn't qualify, any effort to improve your production processes, make them more efficient, reduce waste, or enhance quality could involve qualifying R&D. If you've faced technical challenges and experimented with solutions, that's R&D.
"We only make things to order; it's all bespoke."
Developing custom solutions for customers often involves significant R&D. If you're designing a unique product or adapting your processes to meet a client's specific, technically challenging requirements, that's a strong indicator of qualifying activity.
"We're not inventing anything brand new from scratch."
R&D isn't just about groundbreaking inventions. Significant improvements to existing products, processes, or software can also qualify. If you're making something appreciably better, more reliable, or more efficient, you're likely undertaking R&D.
"Our projects are too small."
There's no minimum size for an R&D project. Even small-scale improvements and problem-solving efforts can qualify if they meet the eligibility criteria. The cumulative effect of many small innovations can lead to a substantial claim.
Real Client Success Story
At Schapira CPAs, we recently worked with a metal fabrication company. Their Managing Director was convinced their work was "just standard fabrication." However, after a detailed discussion, we uncovered significant R&D related to:
- • Developing new welding techniques for a particularly challenging alloy
- • Designing custom jigs to improve the accuracy of complex assemblies
These activities, which they considered "just part of the job," resulted in a substantial tax credit that they reinvested into new equipment.
What Actually Qualifies: The Four-Part Test Made Simple
To determine if a specific project or activity qualifies for R&D tax credits, HMRC uses a set of criteria often referred to as the "four-part test." While the official language can be dense, the underlying concepts are quite straightforward when applied to a manufacturing context.
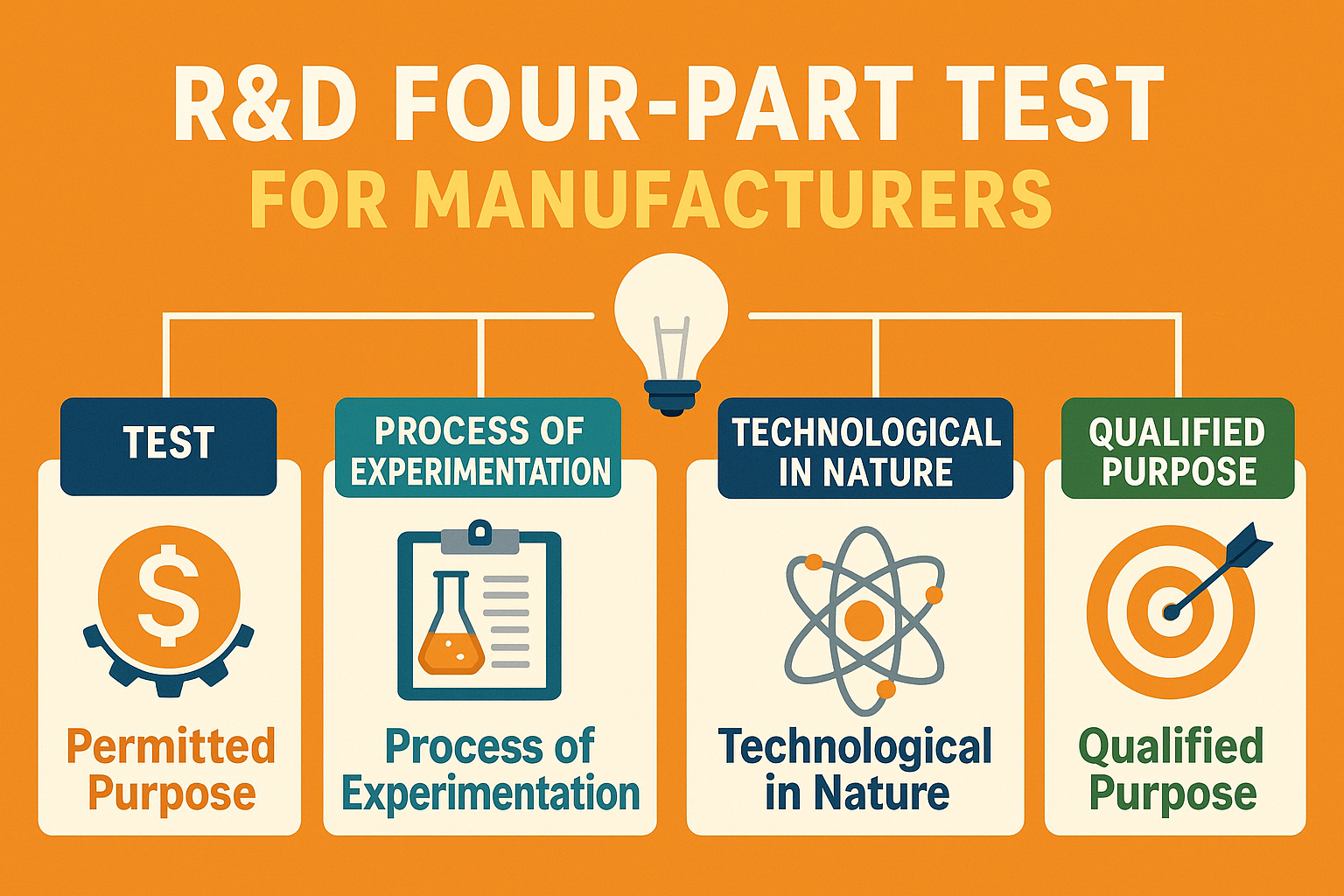
Permitted Purpose
Seeking an Advance in Science or Technology
Are you trying to make something new, or make an existing product or process significantly better, more efficient, or more capable?
- • Developing new biodegradable packaging materials
- • Designing processes to reduce energy consumption by 30%
- • Creating algorithms to optimize CNC cutting paths
Technical Uncertainty
Resolving Scientific or Technological Uncertainty
Did you face a problem where the solution wasn't immediately obvious? Did you have to figure outhow to do something?
- • Uncertainty about optimal welding parameters for new alloys
- • Unknown integration challenges between different systems
- • Unclear material behavior under specific conditions
Technological Nature
Systematic, Investigative, or Experimental Activity
Is your problem-solving approach rooted in engineering, physics, chemistry, or computer science principles?
- • Applying engineering principles to design new gear systems
- • Using material science to evaluate alternative polymers
- • Employing computer science for custom control software
Process of Experimentation
Competent Professionals
Did your engineers, designers, or technicians systematically try different approaches, build prototypes, or conduct tests?
- • Testing different CNC tool paths systematically
- • Conducting trials with varying process parameters
- • Developing and testing multiple prototype iterations
Common Manufacturing Activities That Qualify
Now that we've demystified the four-part test, let's look at concrete examples of everyday activities within a manufacturing environment that often qualify for R&D tax credits. The key is to look for the underlying technical challenges and the systematic approach used to overcome them.
Product Development & Improvement
New Product Design & Development
Conceptualizing, designing, prototyping, and testing entirely new products to meet market demands or leverage new technologies.
Designing a new, more energy-efficient electric motor for industrial applications, facing uncertainties in achieving desired power output while minimizing heat generation.
Existing Product Enhancements
Making significant improvements to existing products to enhance performance, reliability, or reduce costs.
Re-engineering an existing chair design to use a new, sustainable composite material, facing uncertainties about long-term durability and molding methods.
Custom Solutions for Customers
Designing bespoke products or significantly modifying existing ones to meet unique and technically challenging customer specifications.
Creating a highly specialized component for a medical device, requiring development of new machining processes to achieve unprecedented tolerances.
Prototype Development & Testing
Building and rigorously testing functional prototypes to validate designs and refine products before full-scale production.
Developing automated packaging equipment through multiple prototype iterations, testing different sensor configurations for reliable high-speed operation.
Process Improvements
Manufacturing Efficiency Projects
Developing or significantly improving manufacturing processes to increase throughput, reduce cycle times, or lower production costs.
Developing an automated sorting system using machine vision and AI to increase speed and accuracy of quality grading in food processing.
Quality Improvement Initiatives
Developing new methods to enhance product quality, reduce defect rates, or meet more stringent quality standards.
Developing a new, non-destructive testing method using advanced sensors to detect internal flaws in circuit boards previously undetectable.
Tooling & Equipment Development
Custom Tooling Design
Designing bespoke tools, dies, jigs, or fixtures necessary to produce new products or enable new manufacturing processes.
Designing a complex injection mold with innovative cooling channels to reduce cycle times and prevent warping in thin-walled components.
Equipment Modification & Integration
Significantly modifying existing machinery or integrating new equipment where the integration presents technical challenges.
Integrating a high-speed robotic palletizer with existing systems, requiring development of custom communication protocols and control algorithms.
Real Manufacturing Examples: From Skeptic to Success
Sometimes, the best way to understand R&D tax credits qualification is to see how it applies in practice. Here are anonymized examples inspired by real manufacturers we've worked with.
Case Study 1: Precision Engineering Firm & Complex Component Machining
The Challenge
A specialist precision engineering firm serving aerospace needed to machine a complex component from advanced titanium alloy with intricate internal geometries and extremely tight tolerances beyond their existing capabilities.
Initial Stance
Believed their work was "just machining to customer drawings" and therefore not R&D.
The R&D Activities
- • Experimented with novel cutting tool geometries and materials
- • Developed new CNC programming techniques and multi-axis strategies
- • Designed bespoke fixturing to minimize vibration
- • Conducted numerous trials documenting parameters and results
- • Developed new in-process probing techniques
Result
R&D Tax Credit: Over £45,000
Reinvested in advanced metrology equipment to enhance quality control capabilities.
Case Study 2: Food Manufacturer & Innovative Packaging Solution
The Challenge
A chilled food producer needed to develop sustainable packaging using biodegradable film and modified atmosphere packaging technology, facing uncertainties in film performance and gas barrier properties.
Initial Stance
Assumed R&D was only for "new food recipes," not packaging processes.
The R&D Activities
- • Researched and trialed various biodegradable films
- • Modified existing sealing machinery for new film types
- • Conducted extensive shelf-life trials with different gas mixtures
- • Developed new quality control tests for seal integrity
Result
R&D Tax Credit: Approximately £30,000
Helped offset higher sustainable film costs and supported marketing efforts.
Case Study 3: Custom Machinery Builder & Automation Integration
The Challenge
A bespoke machinery builder needed to create an automated system for pharmaceutical vial filling and capping in sterile environments, with precise volume control and integration with legacy track-and-trace systems.
Initial Stance
Unsure if "customer-driven" projects qualified for R&D credits.
The R&D Activities
- • Designed novel peristaltic pump-based filling nozzles
- • Developed custom machine vision algorithms
- • Engineered unique torque-limiting capping mechanisms
- • Experimented with communication protocols for system integration
- • Conducted rigorous testing in simulated sterile environments
Result
R&D Tax Credit: Over £70,000
Significantly improved project profitability and funded development of modular components.

What Doesn't Qualify: Avoiding Common Pitfalls
While the scope for R&D tax credits in manufacturing is broad, it's equally important to understand what activities generally do not qualify. This helps manage expectations and ensures that any claim focuses on genuinely eligible R&D.
Activities That Typically Don't Qualify
Routine, Unchanged Production
Day-to-day manufacturing activities following established processes without any element of technical problem-solving or systematic improvement.
Cosmetic or Stylistic Changes
Alterations that are purely aesthetic without any underlying scientific or technological advancement (e.g., changing product colors or graphic designs).
Market Research & Sales Activities
Activities related to identifying market needs, promoting products, or sales efforts are commercial activities, not R&D.
Standard Quality Control Testing
Routine quality checks to ensure products meet existing specifications. However, developingnew testing methodologies could qualify.
The Assessment Process: Is It Worth Pursuing?
Determining your R&D tax credits qualification involves a methodical assessment of your company's activities. Here's a suggested approach to evaluating your potential for an R&D tax credit claim:
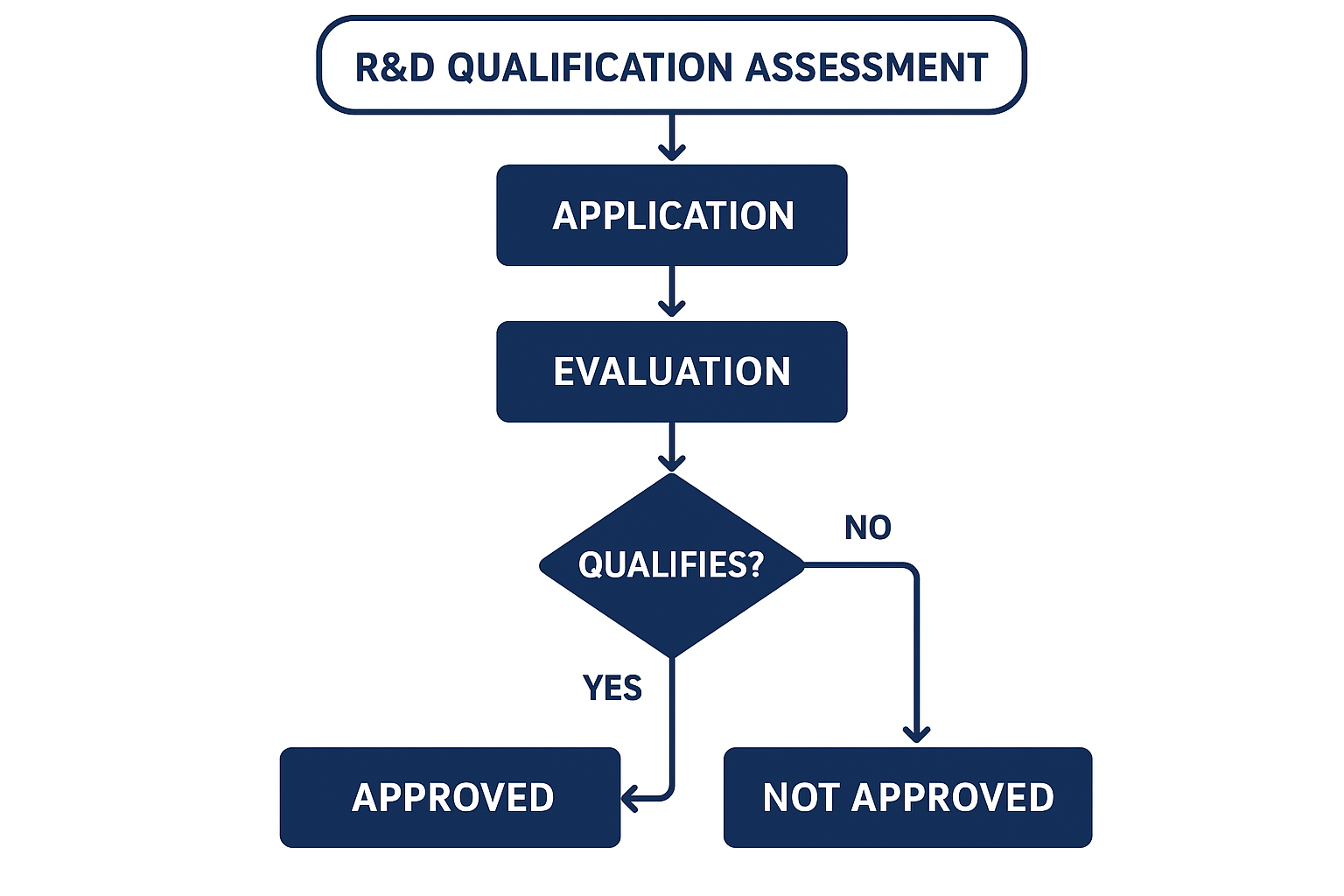
1. Internal Brainstorming
Who to Involve
Gather key personnel from engineering, design, production management, and technical sales.
What to Discuss
- • New products launched or significant improvements made
- • New manufacturing processes implemented
- • Custom tooling, jigs, or fixtures designed in-house
- • Technical problems requiring experimentation
2. Gather Documentation
Useful Documentation
- • Project plans and briefs
- • Design drawings and specifications
- • Test plans and results
- • Lab notebooks or R&D logs
- • Meeting minutes and emails
- • Photographs and videos of prototypes
- • Staff timesheets and project costing records
3. Apply the Four-Part Test
For each identified project, systematically go through the four-part test:
- • Did it aim for a scientific/technological advance?
- • Was there genuine uncertainty?
- • Was the approach technological in nature?
- • Was there systematic investigation by competent professionals?
4. Estimate Qualifying Expenditure
Qualifying Costs Include
- • Staff costs for R&D activities
- • Software directly used in R&D
- • Consumables for prototypes and testing
- • Externally provided workers
- • Subcontracted R&D (with specific rules)
When to Seek Professional Help
While you can start this assessment internally, navigating the complexities of R&D tax credits and preparing a robust claim can be challenging. Consider seeking professional help if:
- • You're unsure if your activities truly qualify
- • You find the documentation requirements overwhelming
- • You want to ensure you maximize your claim while remaining compliant
- • You lack the time or internal expertise
- • You want professional guidance through the entire process
- • You need help liaising with HMRC
Claim Your Free Assessment & Unlock Your R&D Credits
You've learned about the surprising breadth of R&D tax credits qualification for manufacturers. The question remains: Is your manufacturing company leaving valuable money on the table?
Why R&D Credits Matter for Your Business
This isn't just a small rebate; it can be a substantial cash injection or significant reduction in your corporation tax liability, providing vital funds to:
- • Reinvest in further research and development
- • Purchase new machinery or equipment
- • Hire more skilled staff
- • Improve cash flow and business resilience
- • Gain a competitive edge
- • Fund innovation and growth initiatives
Don't let another tax year pass without claiming the credits you deserve. Our manufacturing R&D specialists are ready to help you identify and claim every qualifying activity.
Related Manufacturing Tax Resources
R&D Documentation Best Practices
Essential guide to documenting your R&D activities for successful tax credit claims.
Read Article
Manufacturing Tax Planning Strategies
Comprehensive tax planning approaches specifically designed for manufacturing businesses.
Read Article
Free R&D Documentation Templates
Download our comprehensive templates to help document and track your R&D activities.
Download Templates